Climate action: Mitigation and adaptation
Climate action can take the form of mitigation and adaptation.
In the context of climate action, mitigation means reducing the flow of heat-trapping greenhouse gases into the atmosphere. It can be done by reducing the sources of these gases — for example, reducing the burning of fossil fuels for electricity, heat or transport — or by enhancing the sinks that accumulate and store these gases — for example, the oceans, forests and soil.
- switch to using renewable energy options instead of fossil fuels in transport and industry and for producing electricity
- adopt climate-smart agricultural practices — for example:
- reduce the use of chemical fertiliser and pesticides and replace them with natural solutions
- stop cutting down forests and destroying grasslands
- introduce flood mitigation and flood-safe habitat planning
- develop coastal plantations and conserve mangroves
- use less water-intensive irrigation practices such as drip irrigation
To adapt means to adjust to new conditions. In the context of climate action, adaptation is to adapt one’s life in a changing climate. It involves adjusting to the actual or expected future climate. The goal of adaptation is to reduce our risks from the harmful effects of climate change. Adaptation has many benefits. For example, it can prevent future losses from damage to infrastructure and ill health. If it is done smartly and with a long-term perspective, it provides economic opportunities and helps create a safety net while reducing potential damage.
Examples of adaptation include:
- having disaster management plans and systems in place
- sowing weather-resistant crops
- having weather advisories, early warning systems and health advisories in place
When we take mitigation and adaptation measures, we are building climate resilience. Water conservation, water resource mapping and planning, sourcing local funds for climate action, etc. are both mitigation actions and adaptation actions.
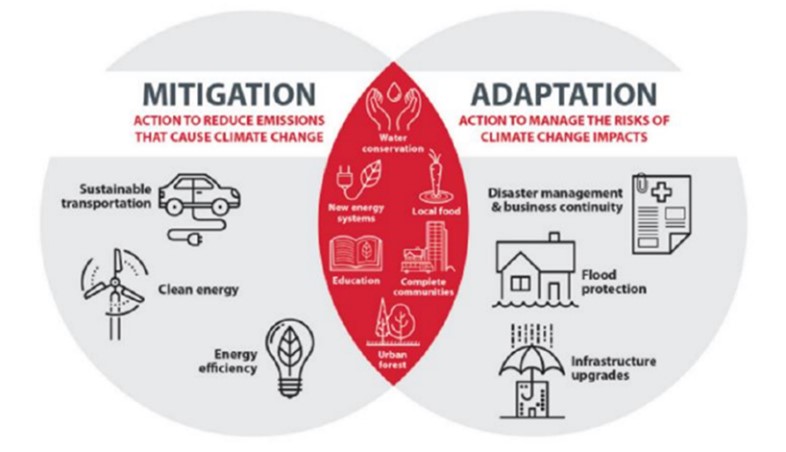
An important point to note about climate action is that it should lead to a reduction in emissions and build communities’ resilience and ability to adapt.
Assessment
![]()
Formative assessment: 3.1
Which of these climate-friendly actions are adaptations?
- Planting crops to suit the changing climate
- Switching to solar-powered energy
- Relocating from high-risk areas
- Planting trees to remove carbon from the atmosphere
Which of the following options do you think are the best way forward to tackle climate change?
- Focus on mitigation
- Focus on adaptation
- Do a mix of both

