Total biomass use
What is biomass?
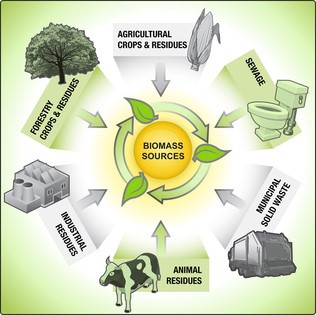
Biomass is renewable organic material that comes from plants and animals. It contains stored chemical energy from the sun that is produced by plants through photosynthesis.
Sources of biomass
- Wood:dead trees, stray branches, stumps, chips and clippings
- Plants: corn, sugarcane, sunflowers, palm nuts, copra (coconut) cotton, rice, wheat
- Waste:solid waste (municipal waste from cities and towns/ garbage) human waste, animal waste from livestock
Plants are a good source of biomass because it takes relatively little energy to harvest them. They also offer a high yield of biomass per hectare.
What is biomass use?
Biomass can be used as a source of energy. By-products from forestry activities, plants and animal waste from farms, even sewage and some waste from landfill can be burned as fuel or used to generate electricity.
Concept of total biomass use
A biomass use system uses agricultural processes to cultivate crops and industrial processes to convert the biomass obtained from farmland into products such as foods, fuels, chemicals and electricity. The industrial processes are usually developed by local entrepreneurs, but sometimes the government finances the industrial process.
In fish markets, for example, more than 60 per cent of by-products are categorised as waste — for example, skin, internal organs, trimmings (usually the head and tail), eggs and bones. This waste can be collected as biomass and converted into feed or agricultural fertilisers. Fish waste biomass is a nutrient-rich, locally available resource.
Adapted from Sahu, B.B., Barik, N.K., Paikaray, A., Agnibesh, A., Mohapatra, S., & Jayasankar, P. (2016). Fish waste bio-refinery products: Its application in organic farming. International Journal of Environment, Agriculture and Biotechnology, 1(4), 837-843. http://dx.doi.org/10.22161/ijeab/1.4.30

Wood pellets made from forest biomass.
Image credit: Viet Nam News. (2023, 19 July). In Vietnam wood pellet industry set for expansion. The Star. https://www.thestar.com.my/business/business-news/2023/07/19/vietnam-wood-pellet-industry-set-for-expansion
The biomass from trees — wood clippings, branches, leaves — can be converted to pellets in a wood pellet mill using technology and specialised machinery. Wood pellets are a type of fuel made from compressed wood which can be used for heating and cooking in domestic stoves and furnaces. They are a good example of total biomass use: they are a form of renewable energy because their source is forest trees and agricultural residues and they are converted into a reusable form, creating minimal wastage.
Rural farmers grow a variety of crops and practise crop rotation so that they can grow a variety of crops suitable for the dry, wet and cold seasons. When many of these crop varieties are harvested, the parts of the plant that are not required are left in the field to dry out or rot. For example, when maize plants are harvested, the cobs, leaves and stalks are left in the fields to dry out or rot because they are not used in the final production of the dry corn as a grain. These parts of the plant are the residue. Agricultural residues are a good source of biomass. They can be converted to fuel to use in stoves for cooking or heating homes or to fodder for livestock. This is an example of optimisation and total biomass use at the farm level.
Farmers who raise livestock like cattle, goats, sheep, poultry and ducks can collect and use waste from their livestock as manure for the crops in the field. This practice is common on a small scale in rural farm settings and is another example of total biomass use.
On a typical farm, waste is generated through crop residues and livestock. This waste is a source of biomass that can be used as fuel or fodder. It can be considered as one way to conserve natural resources within the farm area and, in addition, the by-products of the biomass are returned to the farmland as manure for crops or fodder for animals. Some agricultural residue can be converted to fuel for burning and cooking.
Animal waste is rich in nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium and can be used as:
- fodder for animals
- an energy source
- fertiliser for crops
The benefits of animal waste or manure include the following:
- It contains valuable nutrients — for example, phosphorous, nitrogen and carbon — that benefit the soil while protecting natural resources.
- Adding animal manure to the soil can increase the soil’s organic matter.
- Manure helps the soil particles become less dense and compact.
- Animal waste increases the ability of water to pass through the soil.

