Data Recovery
Even with the application of data protection and loss prevention techniques, data still gets lost or corrupted and needs to be recovered. Data recovery is the process of retrieving inaccessible, lost, corrupted, damaged or formatted data from storage devices when the data cannot be accessed in the usual way. Data can be recovered from any of the following storage devices:
- Internal (In-built) Hard Disk Drives (HDD)
- Internal Solid-State Drives (SSD)
- External HDDs and SSDs
- Flash memory devices
- Optical Storage Devices
- Floppy Disks
Data recovery is usually required due to physical damage of the storage device or when a logical damage has caused a malfunction of the file system used by the storage device. It could also be needed in case of accidental deletion of data or operating system failure. File corruption can also be caused by certain malware such as viruses. In any case, the goal is to restore data to its normal state and make it accessible. The chances of data recovery usually depend on the data loss scenario. For example, with accidental file deletion, it is easier to recover because when data is deleted, it technically is not wiped permanently from the storage device. It remains on the device until it is overwritten by new data or files. Deleted files can also be easily recovered from the recycle bin. It is important to note that data cannot be recovered after it is overwritten. Therefore, more data should not be saved or transferred into the storage device until the data has been recovered. By avoiding this, you increase the chances of data recovery. Data that was not saved to a location is also impossible to recover. For example, if a document was being modified and had not yet been saved, a power outage could lead to permanent loss of the changes. It is advised that we enable automatic saving, and still remember to frequently save any documents that we are working on to prevent inconvenience and data losses.
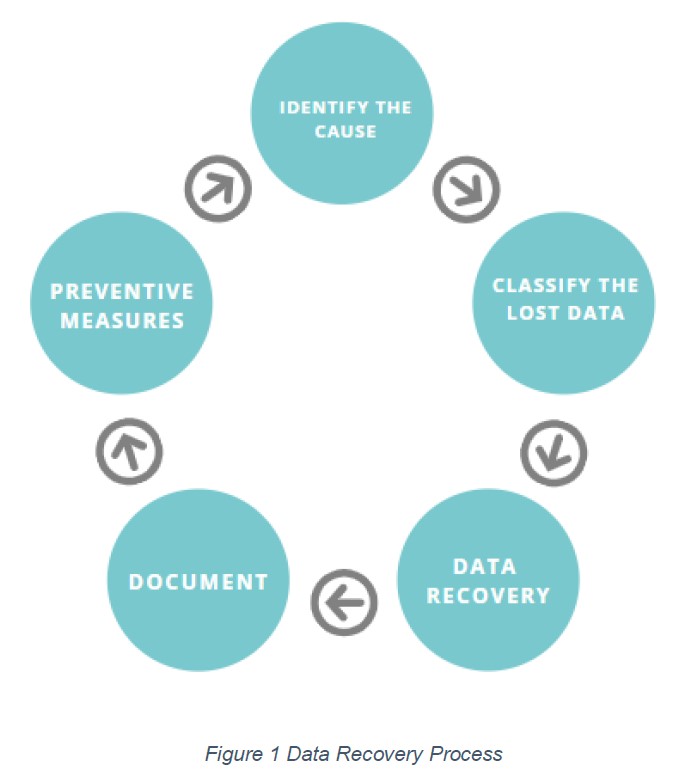
What is the procedure used to recover data? The figure below shows the five steps used to recover data.
1. Identify the cause
The first step to data recovery is determining the cause of the data loss. The cause will inform the tools to use. Evaluate whether data is recoverable or to count your losses. If you cannot identify the cause, it might be best to consult a data recovery expert to avoid permanent data loss.
2. Classify the lost data
Identify the important data stored in the device so as to prioritize data recovery. For example, curriculum development files will have a higher priority to music. Once lost data has been identified, always check any available backup. If a backup exists, then the whole data recovery process can be foregone and the backup restored.
3. Data recovery solution
The root cause of the data loss will determine the resources needed for recovery. Download any software available online for data recovery. Most software available is comprehensive and provides data recovery for various causes. Data recovery solutions include Recuva, EaseUS Data Recovery Wizard and recoverit.
These tools have free and paid versions. The free versions provide limited capability. However, for simple data recovery, the free version usually suffices. You can also contact your institution’s IT department for help because they are likely to have the tools needed to perform data recovery.
4. Document
Document the process used to recover the data. In case of any mistakes, you can be sure of what happened. If you take the device to an expert, you can better explain what you have tried.
5. Preventive measures
After data recovery, enforce measures to prevent the same scenario from happening again. These preventive measures include data backups and partitioning.
Data recovery is time-consuming and can be overwhelming. It is thus better to have backups of all confidential and sensitive data to avoid the hassle. To watch a video on data recovery, use the links below: